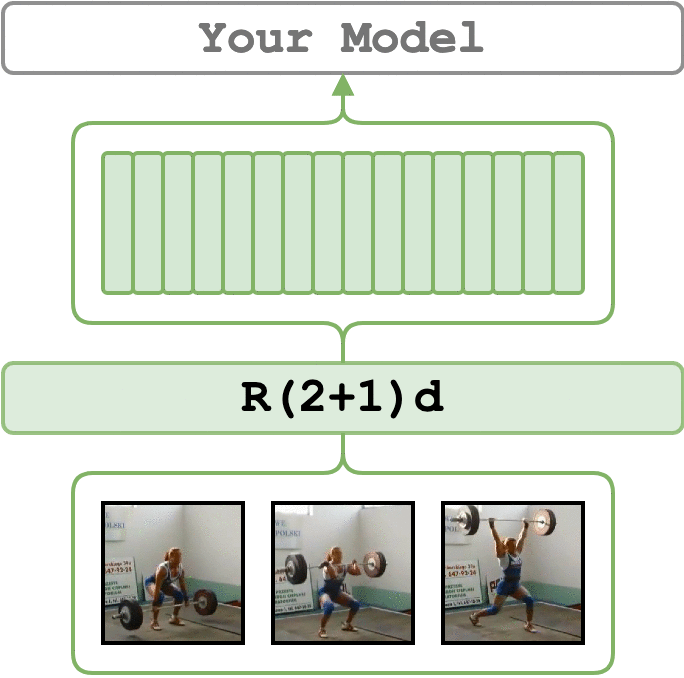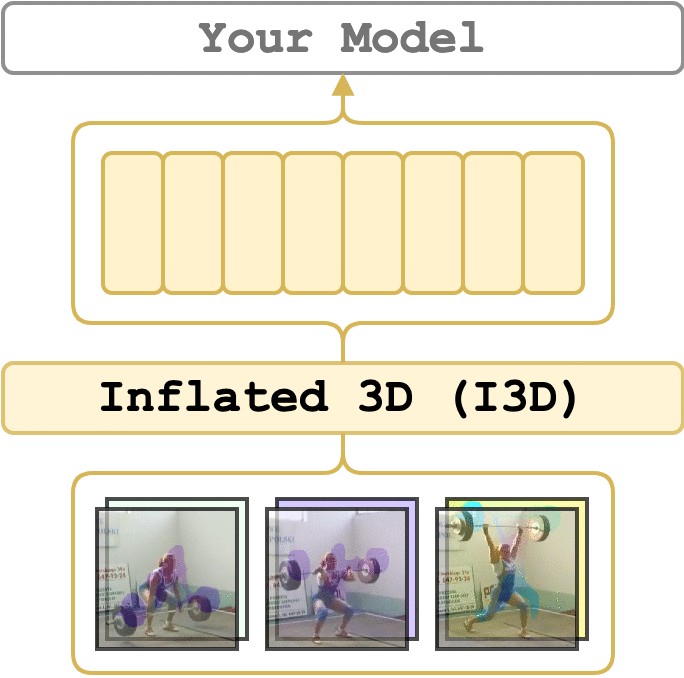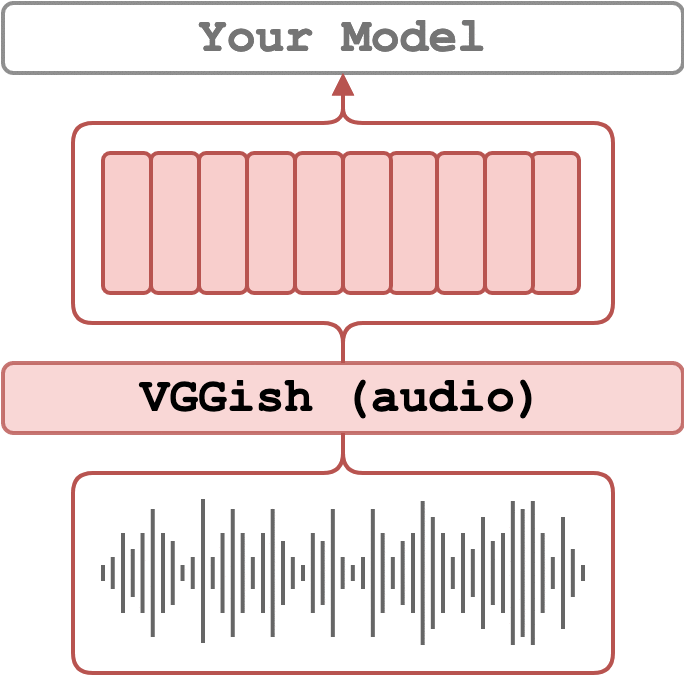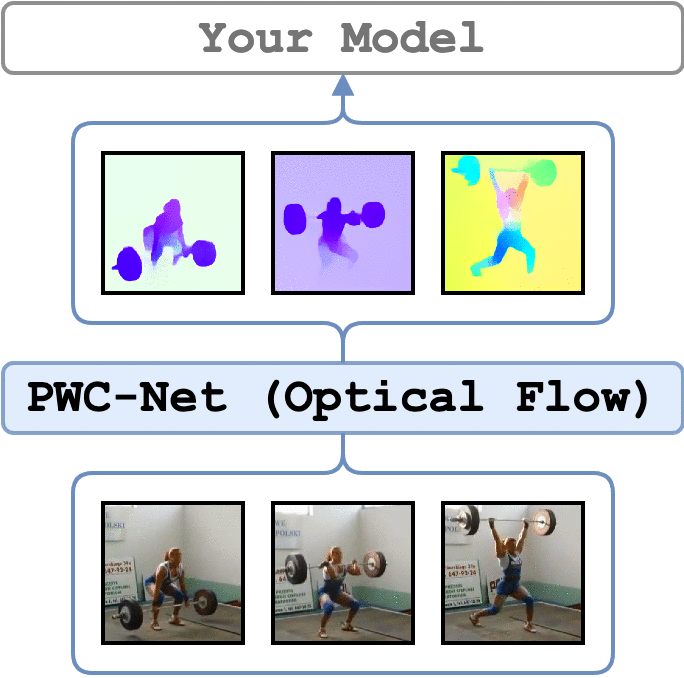


video_features allows you to extract features from video clips.
It supports a variety of extractors and modalities,
i.e. visual appearance, optical flow, and audio.
See more details in Documentation.
Action Recognition
Sound Recognition
Optical Flow
Frame-wise Features
- All models from TIMM e.g. ViT, ConvNeXt, EVA, Swin, DINO (ImageNet, LAION, etc)
- CLIP
- ResNet-18,34,50,101,152 (ImageNet)
or run with conda locally:
# clone the repo and change the working directory
git clone https://github.com/v-iashin/video_features.git
cd video_features
# install environment
conda env create -f conda_env.yml
# load the environment
conda activate video_features
# extract r(2+1)d features for the sample videos
python main.py \
feature_type=r21d \
device="cuda:0" \
video_paths="[./sample/v_ZNVhz7ctTq0.mp4, ./sample/v_GGSY1Qvo990.mp4]"
# if you have many GPUs, just run this command from another terminal with another device
# device can also be "cpu"If you are more comfortable with Docker, there is a Docker image with a pre-installed environment that supports all models. Check out the Docker support. documentation page.
With video_features, it is easy to parallelize feature extraction among many GPUs.
It is enough to start the script in another terminal with another GPU (or even the same one)
pointing to the same output folder and input video paths.
The script will check if the features already exist and skip them.
It will also try to load the feature file to check if it is corrupted (i.e. not openable).
This approach allows you to continue feature extraction if the previous script failed for some reason.
If you have an access to a GPU cluster with shared disk space you may scale extraction with as many GPUs as you can by creating several single-GPU jobs with the same command.
Since each time the script is run the list of input files is shuffled, you don’t need to worry that workers will be processing the same video. On a rare occasion when the collision happens, the script will rewrite previously extracted features.
The inputs are paths to video files. Paths can be passed as a list of paths to videos or as a text file formatted with a single path per line.
Output is defined by the on_extraction argument; by default it prints the features to the command line.
Possible values of output are ['print', 'save_numpy', 'save_pickle']. save_* options save the features in
the output_path folder with the same name as the input video file but with the .npy or .pkl extension.
Please, let me know if you found this repo useful for your projects or papers.
- @Kamino666: added CLIP model as well as Windows and CPU support (and many other useful things).
- @ohjho: added support of 37-layer R(2+1)d favors.
- @borijang: for solving bugs with file names, I3D checkpoint loading enhancement and code style improvements.
- @bjuncek: for helping with timm models and offline discussion.
If you find this project useful in your research, please consider cite:
@misc{videofeatures2020,
title = {Video Features},
author = {Vladimir Iashin and other contributors},
year = {2020},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/v-iashin/video_features}},
} https://github.com/v-iashin/video_features
https://github.com/v-iashin/video_features